Collecting Social Security payments is an important component of any retirement income strategy, but the program can also be complicated to understand.
Below are commonly asked questions and answers to help you prepare for your retirement:
1. When should I collect Social Security benefits?
The answer is different for every individual because it depends on several personal factors. Here are the general milestones:
- Age 62: You can collect Social Security retirement benefits as early as age 62, at a reduced level.
- Full retirement age: If you wait until your full retirement age, as defined by the Social Security Administration, you will receive your full benefit amount.
- Age 70: The retirement benefit amount increases each year if you wait beyond full retirement age (up to age 70) to start collecting.
Waiting for a larger benefit may not be right for everyone. Here are a few factors we’ll consider together as your retirement draws closer:
- Varying tax rates on Social Security income
- Capital gains and IRA withdrawals
- Health issues
- Life expectancy in your family history
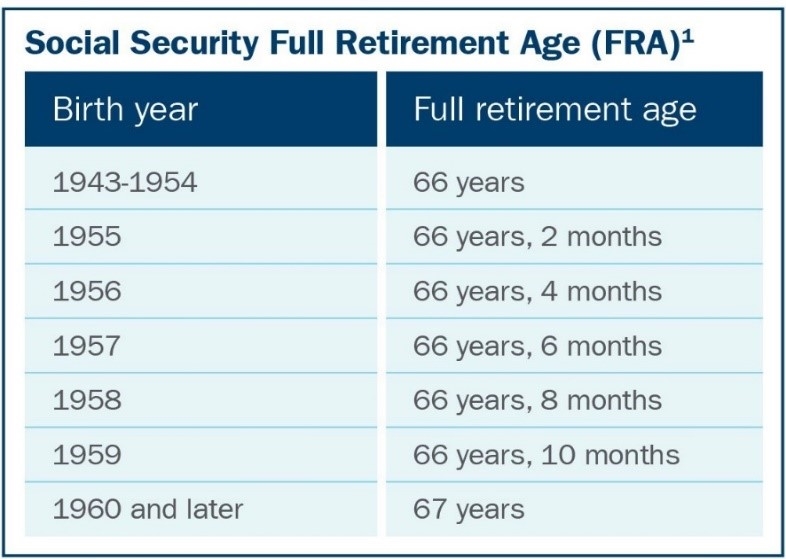
2. What is my full retirement age (FRA)?
The year and month you reach full retirement age depends on the year you were born.
3. Can I change my mind later?
If your circumstances have changed, there are a couple of options available to you.
You have up to 12 months to withdraw your Social Security application if you change your mind. If you received benefits, you are required to repay them.
After you reach your full retirement age, you can also suspend your retirement benefits for a period of time before restarting them later for a higher benefit payment. Suspended benefits will automatically start again at age 70.1
4. Can I work and collect Social Security retirement benefits?
Yes, you can work while collecting Social Security retirement benefits. Here are key considerations:
- Younger than full retirement age (FRA) for the entire year: Your benefits are reduced for earnings above an annual limit ($22,320 in 2024).
- Younger than FRA for part of the year: In 2024, benefits are reduced $1 for every $3 you earn above $59,520. Earnings are counted up to the month before your FRA.
- FRA and older: Beginning with the month you reach full retirement age, your earnings no longer reduce your benefits — no matter how much you earn.
If you’re self-employed, only your net earnings count toward reduced benefits. The Social Security Administration does not count income from government/military benefits, pensions, annuities, capital gains, investment income or interest.
5. Is inflation factored into Social Security?
The Social Security Administration can enact yearly benefit increases called cost-of-living adjustments (COLA) based on inflation. The cost-of-living adjustment for 2024 is 3.2%.2 Since 1975, COLAs have ranged from 14.3% (1980) to 0.0% (2010, 2011, 2016).
6. Can you outlive Social Security?
Regardless of when you choose to begin taking benefits, you cannot outlive Social Security. Unlike some other income streams, it has the backing of the federal government and is protected against inflation.
Let’s discuss your Social Security options
If retirement is not far off for you, then it’s probably time to connect. In general, it’s wise to meet with us five years ahead of your estimated retirement date to begin planning your Social Security income strategy. One year out from retirement, we’ll work together to decide the appropriate age for you to begin claiming benefits.